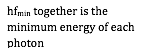The Structure of the Atom
· All atoms are made up of protons, neutrons and electrons
· The protons and neutrons and found in the central nucleus and are collectively called nucleons
· Electrons orbit the nucleus
· The diameter of an atom is ~10-10m, a nucleus ~10-14m and a nucleon ~10-15m
|
|
Proton |
Neutron |
Electron |
|
Charge |
+ 1.60 x 10-19C |
0 C |
-1.60 x 10-19C |
|
Relative Charge |
+1 |
0 |
-1 |
|
Mass |
1.67 x 10-27kg |
1.67 x 10-27kg |
9.11 x 10-31kg |
|
Relative Mass |
+1 |
+1 |
0.0005 |
· Atoms contain equal numbers of protons and electrons making them electrically neutral
· Atoms with more or less electrons than protons are called ions and are charged.
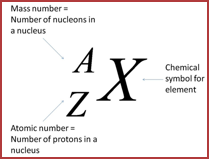
Elements are defined by the number of protons they contain
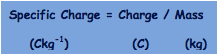 |
This is the ratio of a particles, atom or ions charge (in C) to its mass (in kg)
· A neutrino is a fundamental particle that has no charge and (almost) no mass
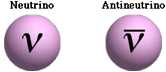 |
They do have energy and momentum
· The symbol used in equations to denote neutrinos and anti-neutrinos are:
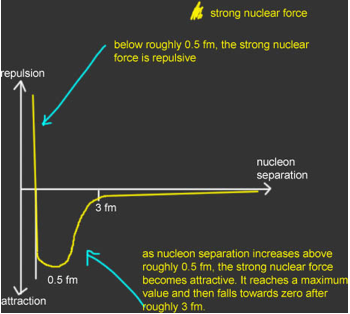 |
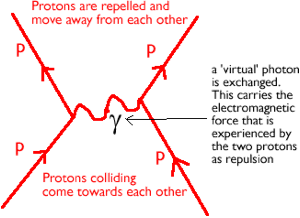
·Atomic nuclei are made of +ve protons and neutral neutrons. The protons therefore repel due to the electromagnetic force. They are only held together because they are made from quarks and therefore the strong nuclear force acts. It is much stronger than the electromagnetic force.

 |
To do:
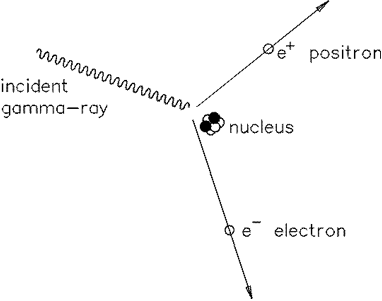
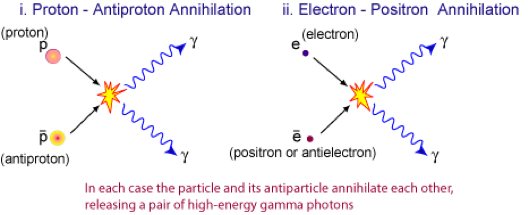
1. Show that a photon must have a minimum energy of 1.02MeV to create an electron-positron pair.
2. Calculate the frequency of such a photon.
3. Calculate the minimum
energy of each photon created when a proton and an anti-proton annihilate.